9+ dicot stem diagram
Root vegetables such as carrots. They are also known as rosette forms some of the many conditions that result from very short internodes ie.

Herbaceous Dicot Stem Young Helianthus Cross Section You Flickr
They have well-developed roots stem and leaves for the conduction of food and water.

. A Name the colour of dry cobalt chloride paper. Divide students into groups of three or four. Leaf is a green dissimilar exogenous lateral flattened outgrowth which is borne on the node of a stem or its branch and is specialised to perform.
TS of Leaf a Dicot and b Monocot. They reproduce with the help of spores present along the back or posterior surface of the leaves. It is also the process of reactivation of metabolic machinery of the seed resulting in the emergence of radicle and plumule.
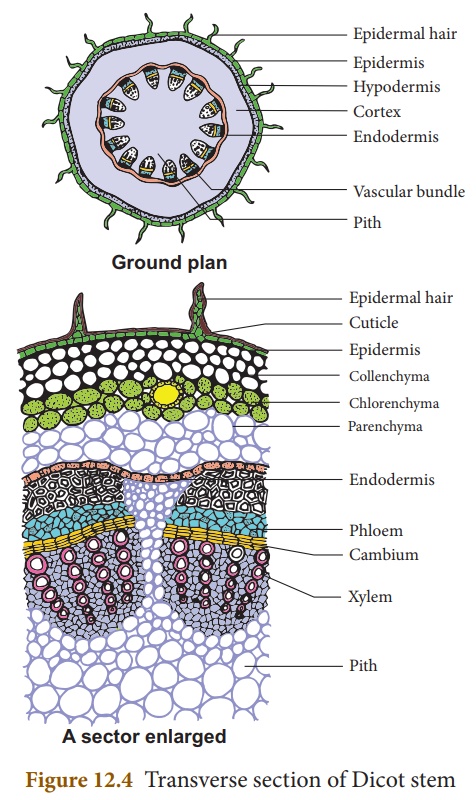
In dicot stem the pith is large and well developed. The below mentioned article provides study notes on Secondary Growth in Dicot Stem of plants. In monocot stem the vascular bundles are scattered and the ground tissue is not marked into different parts.
Protonemal cell of a moss. In Opuntia leaves are. Anatomy of Monocot and Dicot Plants.
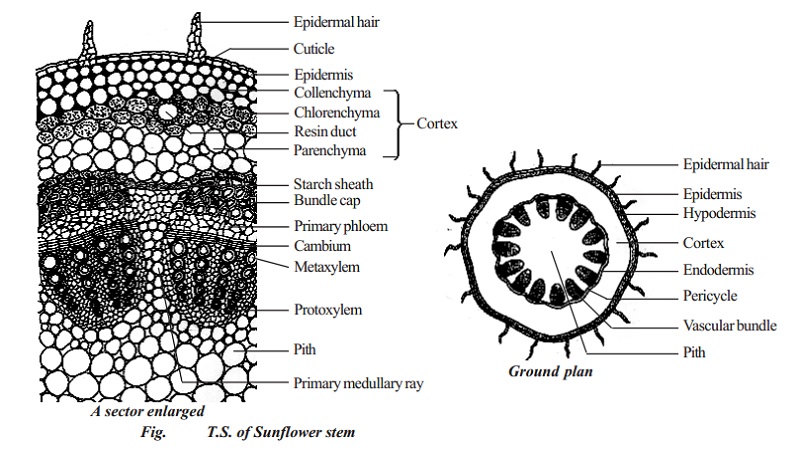
1326 are oval to elongated in shape and green to red in colour. To study the transverse section of a dicot stem a sunflower stem. B Is the experimental leaf a monocot or a dicot.
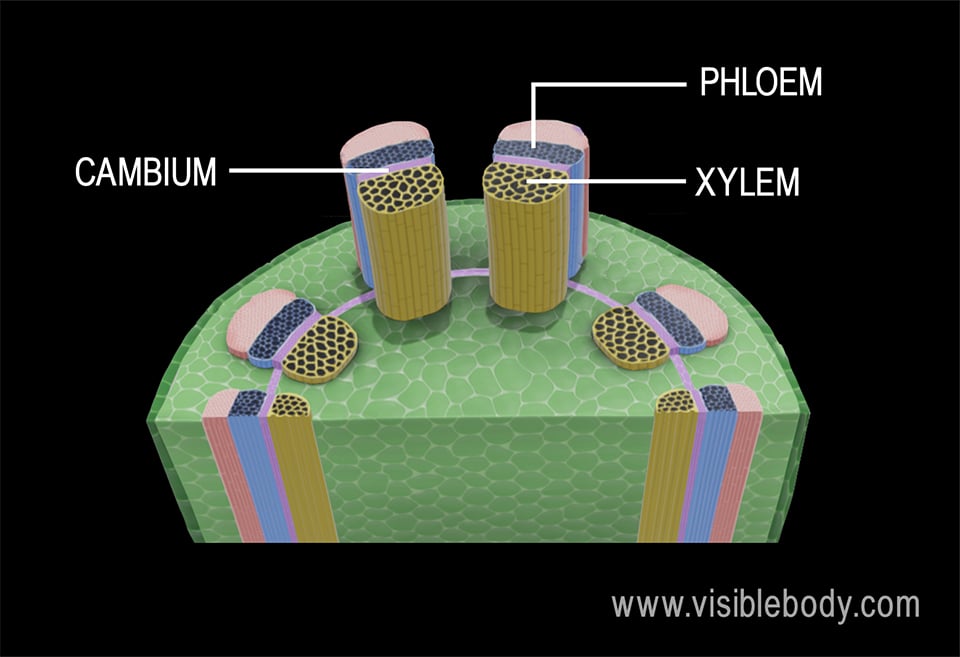
Both xylem and phloem are complex tissues which composed of more than one types of cells. Characteristics of Leaf 3. If a thin and uniform transverse section is taken from a young sunflower stem and observed under the.
B phloem parenchyma is absent. Primary growth produces growth in length and development of lateral appendages. The present post describes the similarities and differences between Xylem and Phloem.
In pea flower the aestivation in corolla is known as vexillary. Gemma cell in Marchantia. Close distances between nodes on the plant stemSee also radical where leaves arise apparently without stems.
It is made up of parenchymatous cells with intercellular spaces. The transverse section depicts the arrangement of different tissues in a particular way from the exterior to the centre as listed below. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule after the embryo sac is fertilized by sperm from pollen forming a zygote.
Acaulescent the leaves and inflorescence rise from the ground and appear to have no stem. What Are Adeventitious Roots. Xylem and Phloem are the components of the vascular tissue system in plants.
The ATP and NADPH. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow. In monocot roots large pith is present.
Citation neededThe stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes. Throughout the day students will see how the food coloring travels up the stem into the leaves and flowers. The related ploidy is as follows.
Aphananthous of flowers Inconspicuous or unshowy as opposed to phaneranthous or showy. The feeder is a protuberance-like structure present in between root and stem tips. Young Sunflower Stems Figs.
A biologist would classify the plant stem shown as a DICOT stemUser. And minerals are transported up a stem into the leaves. In this article we will discuss about the two typical dicotyledonous plants which been selected for the study of internal structure of stem with the help of diagrams.
Aphlebiae Imperfect or irregular leaf endings commonly found on ferns and fossils of ferns from the Carboniferous Period. In most leaves the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the. The seed of a vascular plant is a small package produced in a fruit or cone after the union of male and female reproductive cells.
The outline of the stem in the transverse section is circular with a hairy surface. A feeder develops after the formation of stem and root tips Fig. Extra symbols and characteristics of flowers used in Botany.
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits and form the clade Angiospermae ˌ æ n dʒ i ə ˈ s p ɜːr m iː commonly called angiospermsThe term angiosperm is derived from the Greek words angeion container vessel and sperma seed and refers to those plants that produce their seeds enclosed within a fruitThey are by far the most diverse group of land. Which type of venation do you observe in dicot leaf. Exercises Answers 1.
A typical example of a dicot stem is a sunflower. They do not bear flowers and fruits. In the young parts of the stem the xylem and phloem are together organized as vascular bundles.
BMC Bioinformatics 9 18. What will you identify it as. Stem is the aerial part of the plant and develops from plumule of the.
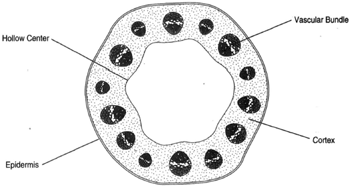
The traverse section is of Monocot stem. It results in the formation of the seedling. Typically the internal structure of leaves comprises the upper epidermis and lower epidermis encompassing the mesophyll cell.
Apical At or on the apex of a. Thus the stem tip two cotyledons feeder root tip and root cap are the parts of a mature embryo. How would a biologist classify the plant stem shownWeegy.
The detailed diagram with the genomic context was shown in. A leaf is a flattened appendage on the stem which is born in the node. In dicot roots the pith is either absent or small.
A chloroplast ˈ k l ɔːr ə ˌ p l æ s t-p l ɑː s t is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cellsThe photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight converts it and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. Secondary growth is the formation of secondary tissues from lateral meristems. The point furthest from the point of attachment.
This process allows plants to grow much faster and is known as vegetative reproduction. Observe the plants carefully and describe them in scientific. Rice wheat maize marigold banana and all monocotyledons are some examples of the fibrous root system.
Leaves is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesisLeaves are collectively called foliage as in autumn foliage while the leaves stem flower and fruit collectively form the shoot system. Definition of Leaf 2. Primary endosperm nucleus in dicot leaf cell of a moss.
Germination is usually the growth of a plant contained within a seed. Mention the ploidy of the following. Based on the constructed phylogenetic tree and the fixage times of monocot-dicot split time.
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant the other being the rootIt supports leaves flowers and fruits transports water and dissolved substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem stores nutrients and produces new living tissue. The transverse section of a plant material shows the following anatomical features a the vascular bundles are conjoint scattered and surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle sheaths. It increases the diameter of the stem.
Solution-The colour of dry cobalt chloride paper is blue. In this article we will discuss about- 1. Meristem cell of monocot ovum of a liverwort and zygote of a fern.
Fibrous roots on the other hand are bushy roots in which thin moderately branching roots grow from the stem. Protonemal cell of a moss - Haploid. The nodes hold one or more.
Acid plant plants with acid saps normally due to the. Cut the bottom of a celery stalk or carnation stem and place in water with food coloring added. A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering along with a food reserveThe formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants the spermatophytes including the gymnosperm and angiosperm plants.
Prothallus cell of a fern. Farmers have taken advantage of some plants that can reproduce without fertilization. Given ahead is the diagram of an experimental set up to study the process of transpiration in plants.
Collect a monocot and dicot plant available in your area. The internal structure of the leaf tells us about the arrangement of the different cells or tissues. In woody plants secondary tissues constitute the bulk of.
Internal Structure Of Dicot Stem Online Biology Notes

Draw A Well Labelled Diagram Of A Typical Dicot Stem

Phloem Definition Function Examples Facts Britannica

Math Physics Chemistry Questions Discussion Lists Dated 2016 09 08

Solved Identify The Labeled Structures In A Prepared Slide Chegg Com
Primary Structure Of Dicotyledonous Stem Sunflower Stem
Monocot And Dicot Stems

2015 American Educational Products Catalog By Michael Warring Issuu

Secondary Growth In Dicot Stem Definition Examples Process Embibe
The Herbaceous Dicot Stem Stems Introduction To Botany Botany Biocyclopedia Com

The Given Below Diagram Shows The T S Of Monocot Stem Some Parts Have Been Indicated By Numbers Select The Answer In Which These Numbers Have Been Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online

Wael Hakros Waelhakros Profile Pinterest

Monocot Vs Dicot Stem Definition Structure 22 Differences Examples

Draw A Well Labelled Diagram Of A Typical Dicot Stem

Dicot Stem Anatomy
Science Catalog Scientific Instrument School Science Lab Manufacturer

Diagram Showing Dicot Stem Structure Stock Vector Image Art Alamy